
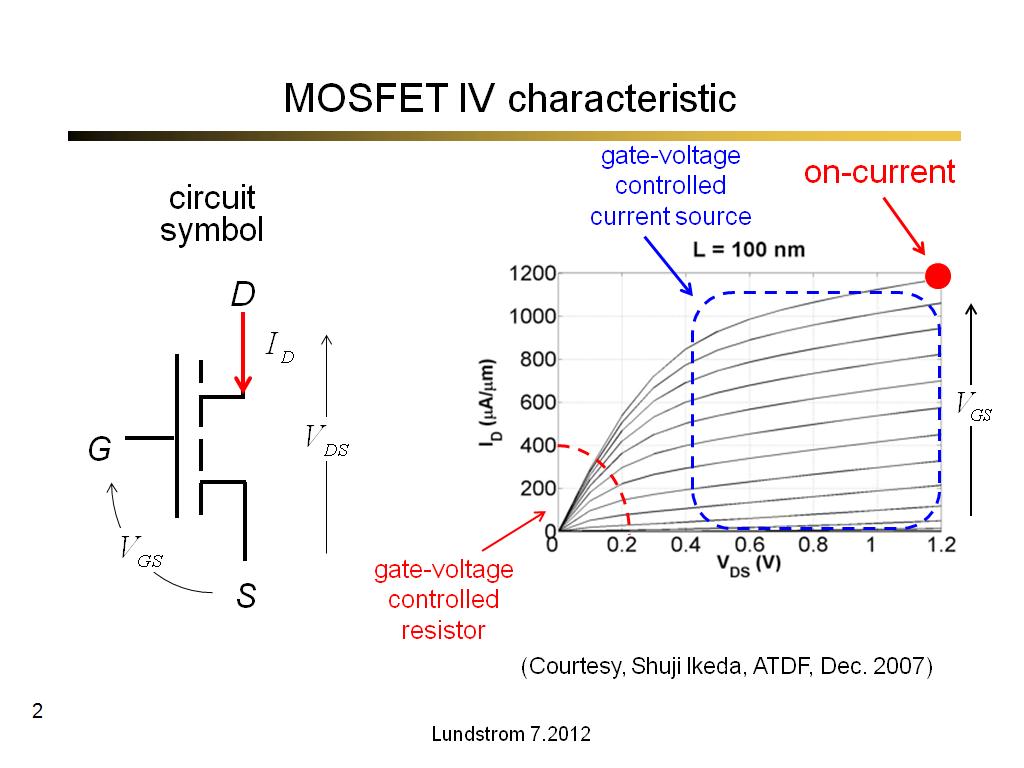
The Gate voltage at which the current reaches zero is called the "pinch voltage", V P. This value will be part of the data supplied by the manufacturer. The current value I DSS represents the value when the Gate is shorted to ground, the maximum current for the device. The gain is proportional to the slope of the transfer curve. The transfer characteristic for the JTET is useful for visualizing the gain from the device and identifying the region of linearity. Modulating the Gate voltage modulates the current flow through the device. This reduces the current flow for a given value of Source-to-Drain voltage.
When the Gate is made more negative, it depletes the majority carriers from a larger depletion zone around the gate.
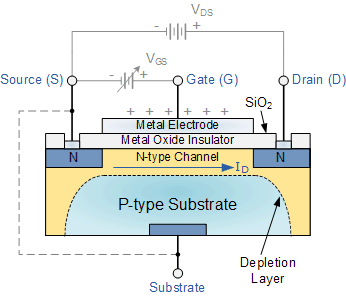
The control element for the JFET comes from depletion of charge carriers from the n-channel. You can see that for a given value of Gate voltage, the current is very nearly constant over a wide range of Source-to-Drain voltages. They have achieved input impedances on the order of 10 15 ohms.Ĭharacteristic curves for the JFET are shown at left. The goal of extremely high input impedance allows an amplifier to sample some signal with minimal "loading" or interference with the signal source.Ĭommon devices using this strategy are called MOSFETs, for metal oxide field effect transistors. The result is a device which has even higher input impedance. The insulated gate field effect transistor (IGFET) differs from the JFET by the addition of a silicon dioxide layer over the JFET and then a layer of silicon nitride. HyperPhysics***** Electricity and magnetism Since the Gate junction is reverse biased and because there is no minority carrier contribution to the flow through the device, the input impedance is extremely high. The current flow consists of the majority carriers (electrons for n-type material). Between the Source and the Drain, the n-type material acts as a resistor. Having a high input impedance minimizes the interference with or "loading" of the signal source when a measurement is made.įor an n-channel FET, the device is constructed from a bar of n-type material, with the shaded areas composed of a p-type material as a Gate. With the reverse biased input junction, it has a very high input impedance. Another device achieved transistor action with the input diode junction reversed biased, and this device is called a "field effect transistor" or a "junction field effect transistor", JFET. In application, the junction transistor has the disadvantage of a low input impedance because the base of the transistor is the signal input and the base-emitter diode is forward biased. The common transistor is called a junction transistor, and it was the key device which led to the solid state electronics revolution.

Field Effect Transistors Junction Field Effect Transistor


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
